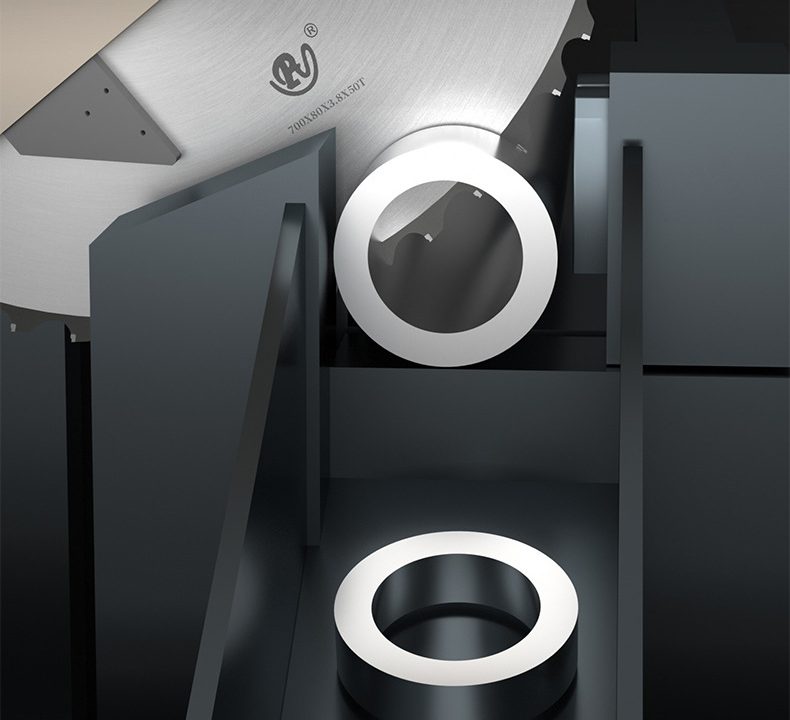
In the modern society, we mostly need to use steel pipes in anywhere for any industries, which means it is a big business to make and cut the steel pipes upon different industrial requests for house building, high-speed roads building, railway building, factory house building, auto manufacturings and many more other industries….And Choosing the best-matching saw blades for cutting steel pipes is crucial to achieving efficient, precise cuts while maintaining tool longevity and ensuring operator safety. Below are key factors to consider when selecting the appropriate saw blade: 
1. Material Composition of the Steel Pipe
- Type of Steel: Different types of steel (carbon steel, stainless steel, alloy steel) have varying hardness levels and properties that require different blade materials and designs.
- Carbon Steel Pipes: Typically softer, allowing for faster cutting speeds with fewer teeth.
- Stainless Steel Pipes: Harder and more abrasive, requiring tougher blades with a higher tooth count for slower, more controlled cuts.
- Alloy Steels: May contain elements like chromium or nickel, which can increase hardness and wear resistance, necessitating specialized blades.
2. Blade Material
- High-Speed Steel (HSS): Suitable for softer steels; offers good durability and heat resistance but may not last long on harder materials.
- Tungsten Carbide-Tipped (TCT): Provides superior wear resistance and durability, especially for harder steels. TCT blades are recommended for most industrial applications.
- Solid Carbide Blades: Offer the highest level of durability and precision but come at a higher cost. Ideal for very hard materials and high-precision work.
- Bi-Metal Blades: Combine the toughness of HSS with the durability of carbide tips, offering a balance between cost and performance.
3. Tooth Configuration and Count
- Tooth Pitch (Teeth Per Inch – TPI): The number of teeth per inch affects the cut quality and speed.
- Low TPI (Fewer Teeth): Faster cutting but rougher finish; suitable for softer steels.
- High TPI (More Teeth): Slower cutting but smoother finish; better for harder steels.
- Tooth Set: The arrangement of teeth can be regular, alternate, or wavy.
- Regular Set: Every other tooth set to one side, providing a wide kerf for fast cutting.
- Alternate Set: Teeth alternately set to either side, offering a balanced cut speed and finish.
- Wavy Set: Groups of teeth set in a wave pattern, reducing vibration and noise, ideal for thin-walled pipes.
4. Cutting Method
- Band Saw Blades: Flexible and suitable for curved cuts or tight radii.
- Circular Saw Blades: For straight cuts with high accuracy and efficiency.
- Reciprocating Saw Blades: Versatile for both straight and curved cuts, often used in demolition or maintenance tasks.
- Abrasive Wheels: Not technically a “blade” but useful for cutting thicker or harder pipes where traditional blades might struggle.
5. Pipe Diameter and Wall Thickness
- Diameter: Larger diameter pipes may require longer blades or specific blade lengths to ensure proper engagement.
- Wall Thickness: Thicker walls demand stronger, more durable blades with appropriate tooth configurations to handle the increased material removal rate.

6. Machine Specifications
- Power Output: Ensure the machine’s power output matches the blade’s requirements to avoid overheating or premature wear.
- Speed Settings: Adjustable speed settings allow for optimal performance across different materials and pipe sizes.
7. Safety Considerations
- Guarding: Proper guarding mechanisms protect operators from flying debris and blade breakage.
- Coolant/Lubrication: Using coolant or lubricants can extend blade life and improve cut quality by reducing friction and heat generation.
- Maintenance: Regular inspection and maintenance of the blade and machinery are essential for safe and effective operation.
8. Economic Factors
- Cost vs. Longevity: While premium blades may have a higher upfront cost, they often offer better durability and lower overall operating costs due to reduced replacement frequency.
- Supplier Reputation: Choose reputable suppliers who provide reliable products and support, including technical advice and after-sales service.
Practical Example
For cutting stainless steel pipes with medium wall thickness, you would likely opt for a tungsten carbide-tipped circular saw blade with a high tooth count (e.g., 60-80 TPI) and an alternate set. This combination ensures a clean, precise cut while handling the material’s hardness effectively.
By carefully considering these factors, you can select the best-matching saw blades tailored to your specific cutting needs, leading to improved productivity, better cut quality, and extended tool life…or you also can directly send message to us for getting the best solution for your machines or steel pipes from us.