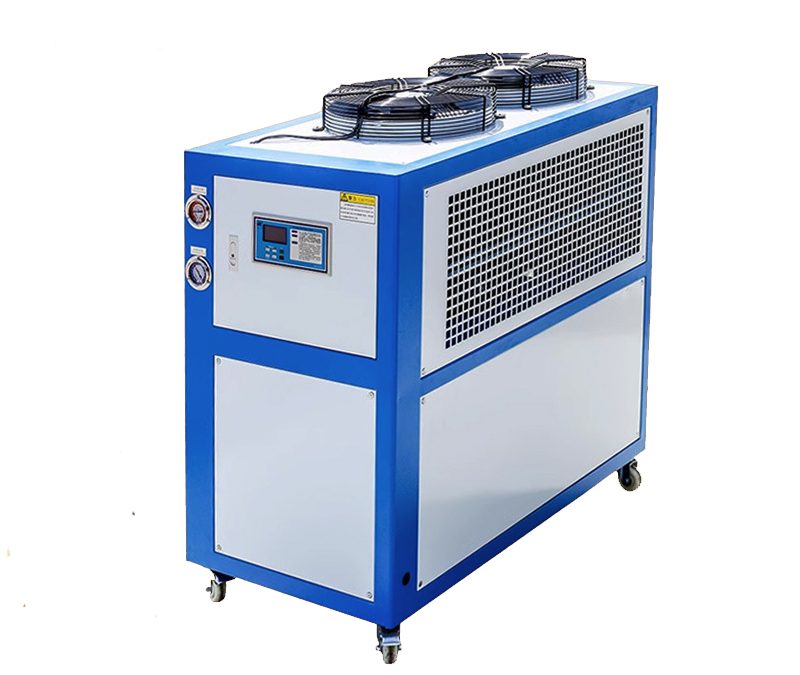
Industrial chiller systems are widely used across many industries to control temperatures in processes that generate heat. These systems are essential for maintaining optimal operating conditions, improving efficiency, and extending the lifespan of equipment. Here are some of the key industries that frequently utilize industrial chillers:
- Manufacturing Industries:
- Plastic Manufacturing: Chillers cool down molds and extrusion lines, helping to shape plastics more efficiently and prevent warping.
- Metalworking: Processes like welding, cutting, and forming generate significant heat, and chillers are used to cool hydraulic fluids and lubricants.
- Automotive Industry: Cooling is required for various manufacturing processes, including paint booths, injection molding, and metal stamping.
- Food and Beverage Industry:
- Processing: Chillers are crucial for cooling pasteurization equipment, fermentation tanks, and other processing machinery.
- Packaging: Cooling is necessary to ensure packaging integrity and to speed up the cooling of hot-filled products.
- Chemical and Pharmaceutical Industries:
- Chemical Processing: Chillers are used to control reaction temperatures and condense vapors in distillation processes.
- Pharmaceutical Production: Temperature control is vital during the synthesis and purification of pharmaceutical compounds.
- Electronics Manufacturing:
- Semiconductor Fabrication: Cooling is essential to prevent overheating of sensitive electronic components during manufacturing processes.
- Circuit Board Assembly: Chillers are used to cool soldering equipment and to maintain temperature stability in clean rooms.
- Printing and Packaging Industry:
- Ink Drying: Chillers help in the quick drying of ink and varnish on printed materials.
- Lamination: Cooling is required to prevent overheating of laminating machines.
- Data Centers and Telecommunications:
- Server Cooling: High-density computing environments generate a lot of heat, and chillers are used to maintain optimal operating temperatures for servers and networking equipment.
- Agriculture and Aquaculture:
- Aquaculture: Chillers regulate water temperature in fish tanks and ponds to ensure the health of aquatic life.
- Storage Facilities: Temperature-controlled storage is necessary for preserving the freshness of agricultural products.
- Healthcare and Hospitals:
- Medical Equipment: Chillers are used to cool imaging devices like MRI and CT scanners, as well as sterilization equipment.
- HVAC Systems:
- Building Cooling: Chillers are a core component of air conditioning systems in commercial and industrial buildings.
- Oil and Gas Industry:
- Refining: Chillers are used to cool oil and gas during refining processes and to maintain the temperature of process fluids.
- Drilling Operations: Cooling is necessary for drilling equipment and to manage the temperature of drilling mud.
- Power Generation:
- Cooling Towers: Chillers are used in cooling towers to reduce the temperature of water used in power plants.
- Turbine Cooling: Chillers cool the air intake for gas turbines to improve efficiency.
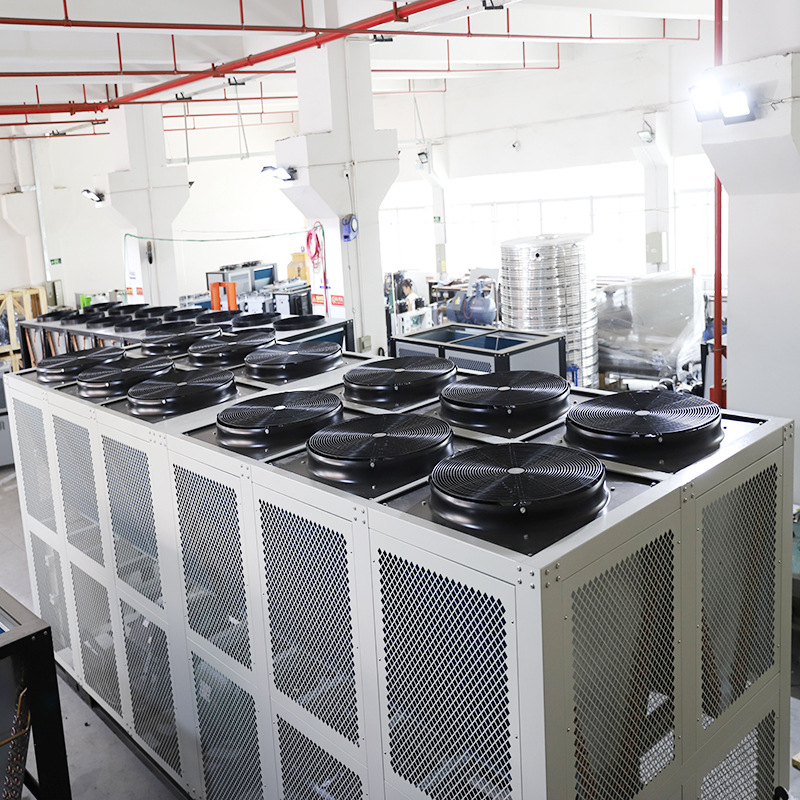 Chillers play a critical role in many industrial processes by providing precise temperature control, which is essential for maintaining product quality, safety, and the longevity of equipment.
Chillers play a critical role in many industrial processes by providing precise temperature control, which is essential for maintaining product quality, safety, and the longevity of equipment.